- Lentivirus
- Adeno-Associated
- Adenovirus
- Pseudovirus
- Vector
- Synthesis
- Autophagy Research
- CRISPR/Cas9
- Noncoding RNA
- Luciferase Assay
- Reagents
WHAT ARE YOU LOOKING FOR?
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a class of endogenous, small RNAs about 20-24 nucleotides in length. A miRNA can target several different genes for regulation, while several miRNAs can regulate the same gene. MiRNA can either bind to the 3'UTR of the mRNA encoding a gene or directly bind to circRNA or lncRNA to regulate the expression of the relevant gene.
The psi-CHECK2 used by Hanbio as luciferase reporter gene vector that adopts a dual luciferase reporter system with F-Luciferase and R-Luciferase, in which R-Luciferase serves as the detection reporter gene while F-Luciferase serves as the internal reference reporter gene. To validate the interactions between miRNA and mRNA/lncRNA/circRNA, the target sequence (3'UTR of the mRNA or lncRNA/circRNA) is inserted into psi-CHECK2 as the 3'UTR of R-Luciferase, with the miRNA's mimics to co-transfect 293T cells. If the expression of luciferase decreases (decrease in fluorescence signal), it suggests that the sequence contains the miRNA's target.
To verify whether there is competitive binding between circRNA/lncRNA and miRNA, can transfect plasmids for overexpressing circRNA/lncRNA that are thought to have competing binding sites on top of transfecting reporter plasmids and mimics or knock down circRNA/lncRNAs that have competing binding sites, and the changes of R-Luciferase activity are observed. Increased activity of luciferase when overexpressing circRNA/lncRNA or decreased activity of luciferase when knocking down circRNA/lncRNA indicates competitive binding of miRNAs between them, and vice versa, there is no competitive binding.
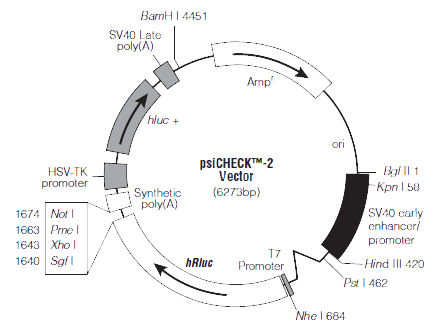
The map of psi-CHECK2 plasmid
Construction of promoter reporter plasmid
Construction of reporter plasmid for miRNA and target genes
Single (Dual) Luciferase Assay Kit
The most common method for verifying the interaction of miRNA with the target gene is the dual luciferase validation assay.
Luciferase is a collective term for enzymes in nature that can catalyze luciferin to produce bioluminescence. The most representative luciferase are from Firefly and Renilla, named F-Luciferase and R-Luciferase, respectively.
These two types of luciferase act in different ways. Firstly, the substrates and cofactors are different. F-Luciferase requires luciferin, O2, ATP, and Mg2+ for functioning, while R-Luciferase only requires coelenterazine and O2. Secondly, the color of bioluminescence is different. F-Luciferase catalyzes yellowish-green light with a emission wavelength of 560 nm, whereas R-Luciferase catalyzes blue light with a emission wavelength of 465 nm. It is often applied to the studys of verifying the activity that regulate the promoter transcription and interaction between the miRNA and the target genes.
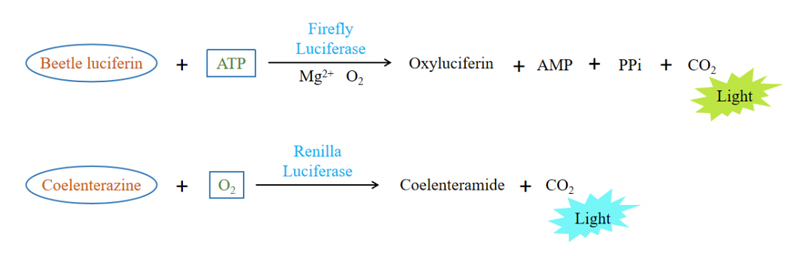
The study of interaction between microRNA and target gene:
Validation of microRNA binding to target genes: Validation of microRNA binding to target genes (mRNA, lncRNA, circRNA)
Research on ceRNA mechanism: validation of competitive binding of microRNAs by different target genes
Service process for Binding Validation of MicroRNA and target gene:

Prediction of binding sites for microRNA and target gene→Construction of reporter plasmids→Transfection and detection
Long non-coding RNA NORAD/miR-224-3p/MTDH axis contributes to CDDP resistance of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by promoting nuclear accumulation of β-catenin
(Journal: Molecular Cancer, IF=27.401, Hebei Medical University)
Hypoxia-induced circWSB1 promotes breast cancer progression through destabilizing p53 by interacting with USP10
(Journal:Molecular Cancer, IF=27.401, Chongqing Medical University)
Small extracellular vesicles deliver osteolytic effectors and mediate cancer‐induced osteolysis in bone metastatic niche
(Journal:J Extracell Vesicles, IF=25.843, Southwest Hospital Third Military Medical University )
Nanoprobes‐Assisted Multichannel NIR‐II Fluorescence Imaging‐Guided Resection and Photothermal Ablation of Lymph Nodes
(Journal: Advanced Science, IF=16.806, Zhejiang University)
A novel inactivated whole-cell Pseudomonas aeruginosa vaccine that acts through the cGAS-STING pathway
(Journal: Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy, IF=12.900, West China Hospital, Sichuan University)

Contact Hanbio and leave your requirements. We will reply as soon as possible.